Impacts of global warming on sea level rise
Impacts of global warming on sea level rise
Sea level rise is a serious issue that is affecting the world’s coastal communities, low-lying areas, and islands
Global warming, caused by the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane, is a major threat to our planet’s climate and ecosystem.
One of the most visible and significant impacts of global warming is the rise in sea level, which is caused by the melting of ice sheets and glaciers, as well as the thermal expansion of seawater. This phenomenon poses a significant threat to coastal communities, low-lying islands, and other areas that are vulnerable to flooding and erosion.
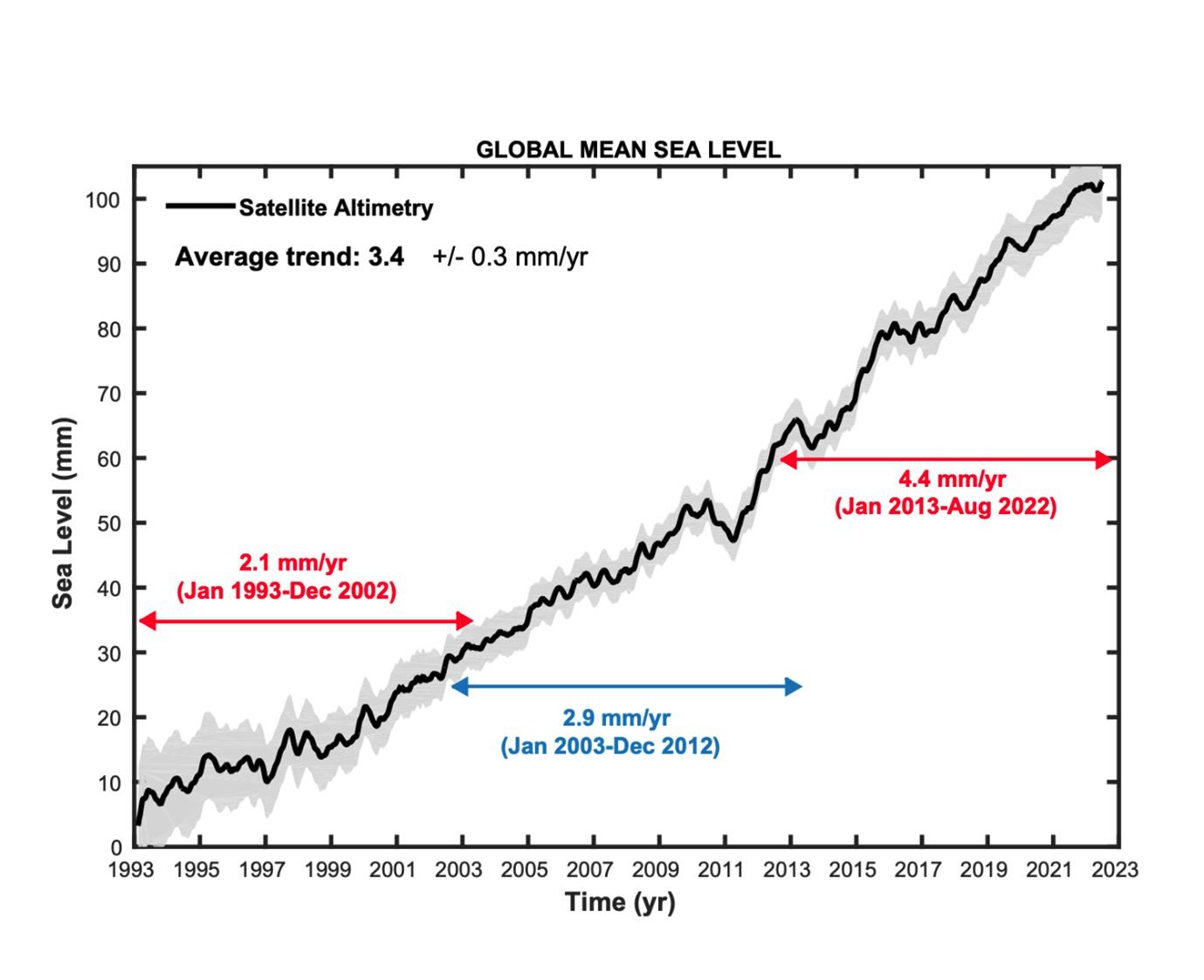
Over the past century, the global sea level has risen by about 8 inches (20 cm), and this trend is expected to continue in the coming decades. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the global sea level is projected to rise by another 1-4 feet (30-120 cm) by the end of this century, depending on the level of greenhouse gas emissions and other factors.
Sea level rise is a serious issue that is affecting the world’s coastal communities, low-lying areas, and islands. The increase in sea level has far-reaching consequences such as the loss of habitats, flooding, and increased storm surges. In this article, we will discuss the impact of global warming on sea level rise and its consequences.
The impacts of sea level rise are already being felt in many parts of the world. In low-lying areas such as Bangladesh, the Maldives, and parts of coastal Africa, flooding and erosion are becoming more frequent and severe, leading to the displacement of millions of people. In cities such as Miami, New York, and Shanghai, sea level rise is exacerbating the effects of storm surges and tidal flooding, causing billions of dollars in damage and disrupting daily life.
Loss of Ice Sheets in Greenland and Antarctica:
One of the main drivers of sea level rise is the melting of ice sheets and glaciers in Greenland and Antarctica. These vast ice sheets contain enough water to raise the sea level by more than 200 feet (60 meters), and their melting is accelerating due to rising temperatures and changing weather patterns. As the ice melts, it flows into the ocean, causing the sea level to rise.
Thermal Expansion of Water:
Another factor contributing to sea level rise is the thermal expansion of seawater. As the ocean absorbs heat from the atmosphere, the water molecules become more energetic and spread out, causing the volume of the ocean to increase. This effect is particularly pronounced in the top few hundred meters of the ocean, which have warmed significantly over the past century.
To address the problem of sea level rise, it is essential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. This can be achieved through a combination of measures, including transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and reducing deforestation and other land-use changes. In addition, we must adapt to the impacts of sea level rise by developing infrastructure and building practices that can withstand flooding and erosion, as well as by relocating vulnerable communities to higher ground.
In conclusion, global warming is causing sea levels to rise, with serious implications for coastal communities, low-lying islands, and other vulnerable areas. The impacts of sea level rise are already being felt, and they are projected to become more severe in the coming decades. To address this problem, we must take urgent action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change. By working together, we can protect our planet and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
[ Se você gostou desse artigo, deixe um comentário. Além disso, compartilhe esse post em suas redes sociais, assim você ajuda a socializar a informação socioambiental ]
in EcoDebate, ISSN 2446-9394
A manutenção da revista eletrônica EcoDebate é possível graças ao apoio técnico e hospedagem da Porto Fácil.
[CC BY-NC-SA 3.0][ O conteúdo da EcoDebate pode ser copiado, reproduzido e/ou distribuído, desde que seja dado crédito ao autor, à EcoDebate com link e, se for o caso, à fonte primária da informação ]