Impacts of ocean warming on global climate
Impacts of ocean warming on global climate
Ocean warming refers to the increase in the temperature of the ocean over time.
This warming is caused by the absorption of heat from the atmosphere, primarily due to the increase in greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide.
This process is known as ocean heat uptake and is a significant contributor to global warming.
Ocean warming can have a number of significant impacts on the global climate, some of which include:
- Rising sea levels: As the ocean warms, it expands, which leads to a rise in sea level. This can have a number of negative impacts, including increased flooding and coastal erosion.
- Changes in ocean circulation patterns: Ocean currents help to regulate the Earth’s climate by transporting heat from the equator to the poles. As the ocean warms, these circulation patterns can change, which can have a number of impacts on weather patterns and climate.
- Changes in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events: Ocean warming can lead to changes in the formation and track of storms, which can increase the frequency and severity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes and typhoons.
- Impact on marine life: Warmer ocean temperatures can alter the distribution and behavior of many marine species, and can also lead to coral bleaching and the death of other marine organisms, which can have a cascading effect on the entire ocean ecosystem.
- Increased acidification: As the ocean absorbs more carbon dioxide, its pH decreases, which can make it more acidic. This can have a number of negative impacts on marine life, as it can make it harder for organisms to build and maintain their shells and skeletons.
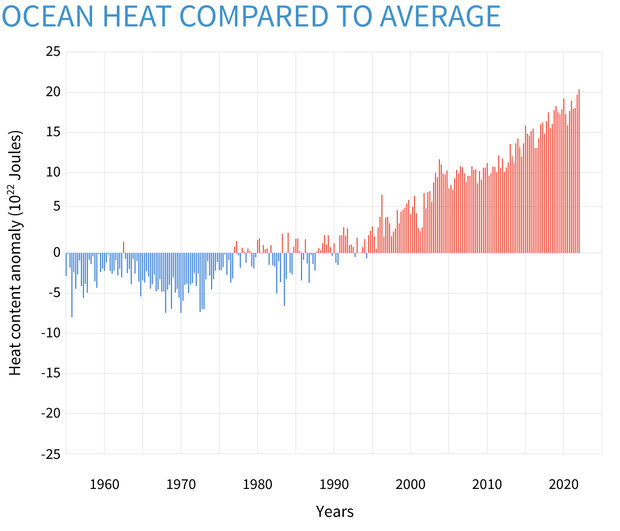
Seasonal (3-month) heat energy in the top half-mile of the ocean compared to the 1955-2006 average. Heat content in the global ocean has been consistently above-average (red bars) since the mid-1990s. More than 90 percent of the excess heat trapped in the Earth system due to human-caused global warming has been absorbed by the oceans. NOAA Climate.gov graph, based on data (0-700m) from the NCEI Ocean Heat Content product collection.
For more information, we recommend that you read the articles below:
Aquecimento dos oceanos atinge novo recorde
Aquecimento global pode interromper a circulação profunda do oceano
Os riscos climáticos do aquecimento dos oceanos
Aquecimento e acidificação dos oceanos impactam a cadeia alimentar marinha
A relação de interdependência do oceano e clima
Aquecimento do Oceano Ártico aumenta nevascas mais ao sul
Calor do oceano, desoxigenação e acidificação são ‘alarmantes’
Aquecimento dos oceanos pode causar extinção em massa de espécies marinhas
Aquecimento dos oceanos pode levar à extinção de corais
Emergência climática: Temperaturas extremas no oceano são o novo normal
Como as mudanças climáticas afetam os oceanos?
Aumento do calor nos oceanos sobrecarrega os sistemas climáticos
[ Se você gostou desse artigo, deixe um comentário. Além disso, compartilhe esse post em suas redes sociais, assim você ajuda a socializar a informação socioambiental ]
in EcoDebate, ISSN 2446-9394
A manutenção da revista eletrônica EcoDebate é possível graças ao apoio técnico e hospedagem da Porto Fácil.
[CC BY-NC-SA 3.0][ O conteúdo da EcoDebate pode ser copiado, reproduzido e/ou distribuído, desde que seja dado crédito ao autor, à EcoDebate com link e, se for o caso, à fonte primária da informação ]